
When a tooth is lost, the surrounding bone is often affected over time. Bone grafting is a form of reconstructive surgery that helps generate and build bone. Bone grafting optimizes bone contour and increases bone quantity, creating the necessary foundation for restorative treatments such as dental implants once the area has healed. Healing time for bone grafts is generally between 4 – 6 months, though it can sometimes take longer.
Bone grafts can be used to:
- Prevent subsequent bone loss following an extraction
- Correct congenital defects
- Repair injuries and trauma
- Prepare for dental implant placement
Bone Regeneration
Bone regeneration is a surgical procedure that regenerates jaw bone and surrounding tissue. Used to encourage the body’s natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue, this procedure is often performed to protect your existing teeth and the tissues that keep them in place. During this procedure, regenerative bone grafting material or bone growth enhancing elements are placed into the weakened area to strengthen and rebuild the bone’s structure.
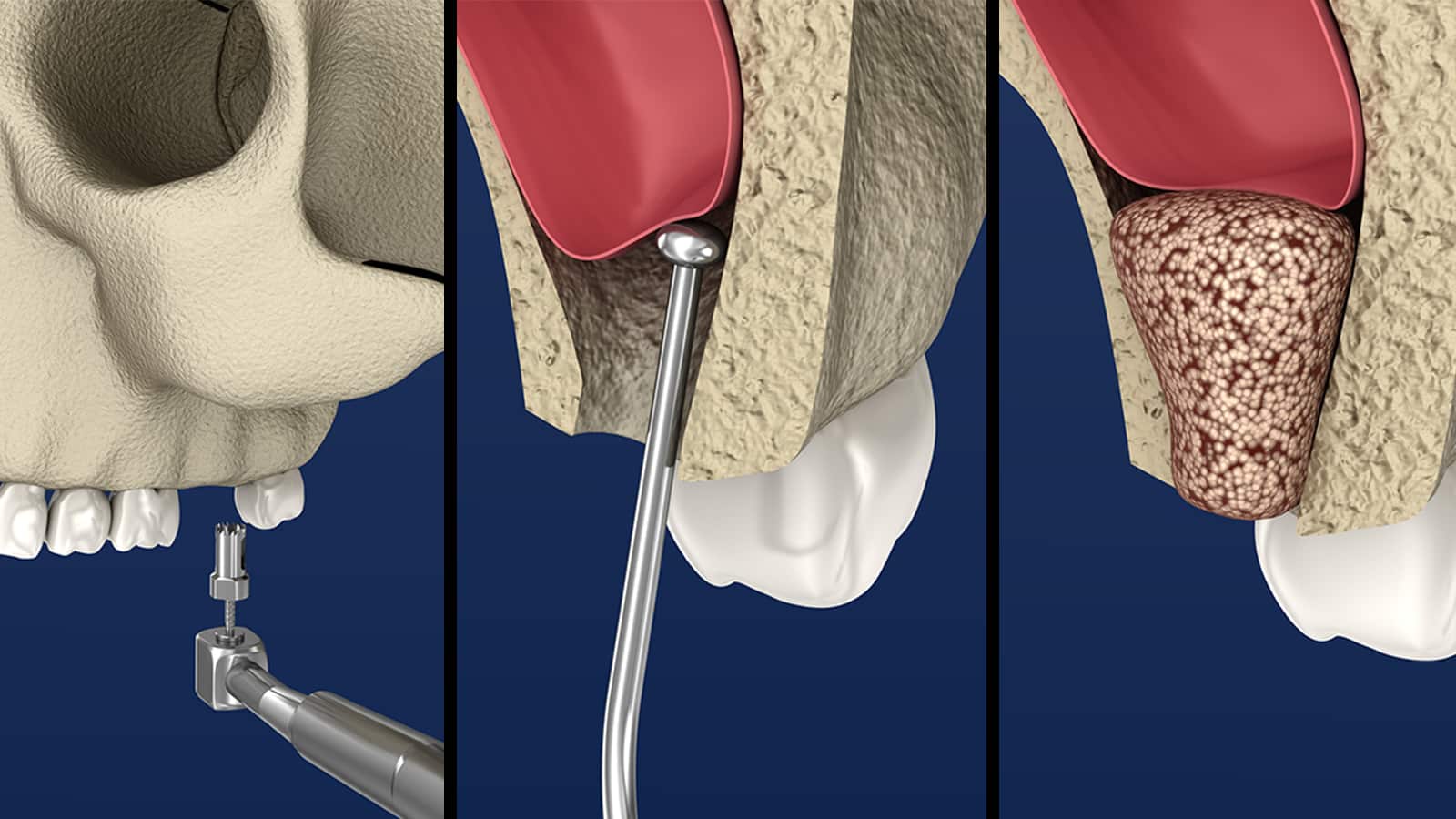
Sinus Augmentation
Sinus augmentation is performed to increase the amount of bone structure in the jawbone. This surgery is usually performed for the purpose of supporting a dental implant, which can be placed once the bone has healed and has sufficient density and volume to support the implants.
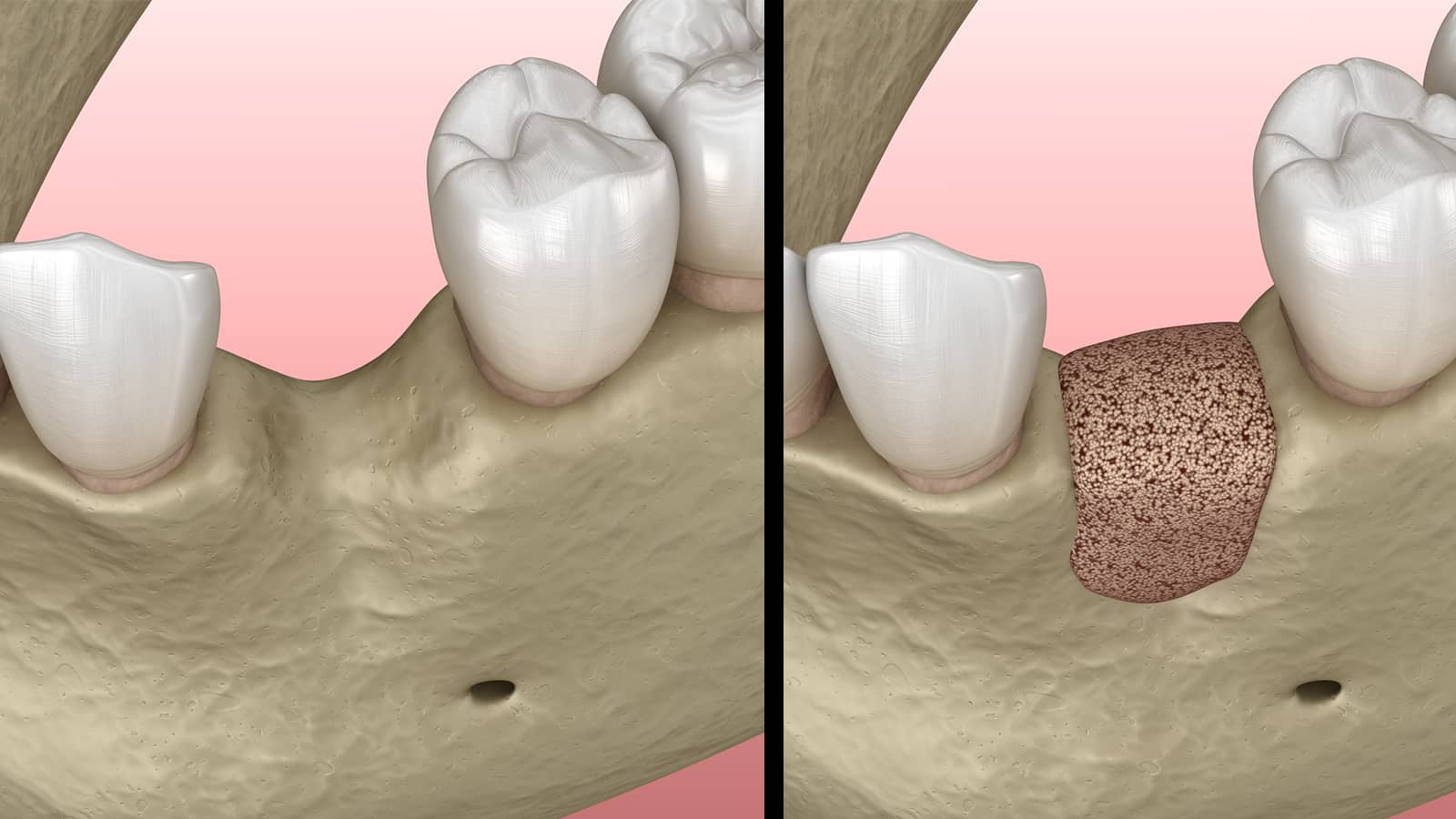
Ridge Preservation
Ridge preservation is typically performed following a tooth extraction to help reduce any subsequent bone loss. Bone grafting material or bone growth enhancing elements are placed into the socket where the extracted tooth was removed to prevent resorption of bone and to stimulate your body’s own natural capacity to regenerate bone. Bone resorption can impact future restorative treatments that require a solid support system such as dental implants, crowns, or bridges.

